The latest news is that PieX AI is the first to apply millimeter-wave radar and device-built AI in the field of consumer wearable products. This is the world's first pendant that uses millimeter-wave radar to achieve AI emotion tracking. This groundbreaking innovative product attracted a large number of visitors to experience it on the day of the CES 2025 conference.
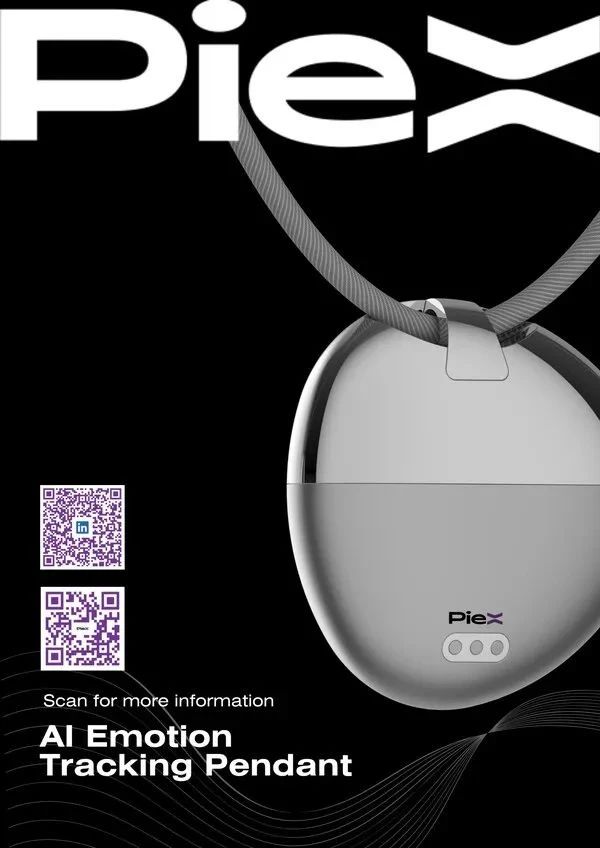

PieX impressed attendees with its unique features, including mood tracking, guided meditation, automatic diary writing, and AI-driven coaching. And it is more than just a pendant, it is a revolutionary emotional wellness tool designed to help people better understand and manage their emotions.
One striking feature is the AI coaching feature, which provides personalized suggestions based on the user's emotional state. PieX integrates multiple technological innovations under its sleek design, including the use of millimeter-wave radar and other sensors to monitor the user's stress level, and on-device large language models (LLM) to provide real-time emotional insights and interactions.
So, what are the main applications of millimeter-wave radar in AI emotion tracking?
The application of millimeter-wave radar in AI emotion tracking is mainly reflected in emotion monitoring, data processing, and multimodal fusion. It can monitor the human body's tiny movements and physiological signals, such as heartbeat and breathing, in a non-contact manner, and then infer the user's emotional state. With the help of the point cloud data generated by the millimeter-wave radar and combined with AI algorithms, high-precision emotion recognition can be achieved. For example, the RF-Emotion system has demonstrated high automation accuracy in estimating heartbeat intervals and inferring emotional states. In addition, millimeter-wave radar data can be integrated with other sensor data (such as cameras) to provide users with a more comprehensive emotion recognition solution.
About using "millimeter wave radar" to achieve "AI emotion tracking"
Technical principle
The application of millimeter wave radar in AI emotion tracking is mainly based on its ability to monitor human physiological signals non-contactly. Specifically, millimeter wave radar can emit radio frequency (RF) signals and analyze the reflection of these signals on the human body to infer the user's emotional state. The key to this technology is the ability to recover the heartbeat waveform from the reflected signal with a low signal-to-noise ratio and separate individual heartbeats. Its accuracy is comparable to that of contact electrocardiogram (ECG) sensors and has good robustness to the user's body movements.
Research results
A study recruited 72 participants for testing. The results showed that the mean absolute error of millimeter wave radar in estimating heartbeat intervals was within 0.56%, and the accuracy of inferring emotional states (calm, fear and happiness) reached 86.50%. This shows that millimeter wave radar can effectively monitor the emotional state of users in daily life or work, providing a new method for non-contact emotion recognition.
Application Cases
At CES 2025, PieX AI launched the world's first emotion tracking pendant based on millimeter wave radar and on-device AI, the PieX Pendant. The pendant integrates multiple technological innovations, including the use of millimeter wave radar and other sensors to monitor the user's stress level, and the large language model (LLM) on the device to provide real-time emotional insights and interactions.
The main features of PieX Pendant include:
Emotion tracking: Real-time monitoring of the user's emotional state.
Meditation guidance: Provide meditation guidance to help users relax.
Automatic diary writing: Record the user's emotional changes.
AI-driven personal coaching: Provide personalized suggestions based on the user's emotional state.
Advantages and Challenges
Advantages:
Non-contact monitoring: Millimeter wave radar does not need to be in contact with the user's body, avoiding the discomfort caused by traditional physiological signal acquisition methods.
High precision: Able to restore heartbeat waveforms with high precision, and the accuracy of inferring emotional states is high.
Real-time feedback: The large language model on the device can provide emotional insights and interactions in real time, helping users better understand and manage their emotions.
Privacy protection: The user's emotional data is processed and stored locally, which ensures the user's privacy and data security.
Challenges:
Technical complexity: The millimeter wave radar signal processing and emotion recognition algorithms are relatively complex, requiring highly professional technical teams to develop and optimize.
Cost: The application of high-precision millimeter wave radar and AI technology may increase the cost of the product and affect its market penetration.
User acceptance: Although non-contact monitoring has advantages, users may have different acceptance of new technologies, and market education and user experience optimization are needed to improve acceptance.
Industry insiders said that millimeter wave radar has broad application prospects in the field of AI emotion tracking. With the continuous advancement of technology and the reduction of costs, such devices are expected to be used in more scenarios, such as smart homes, smart offices, and healthcare. In addition, the development of multimodal fusion technology will further improve the accuracy and reliability of emotion recognition, providing users with more personalized and intelligent emotional health management solutions.
This paper is from Ulink Media, Shenzhen, China, the organizer of IOTE EXPO (IoT Expo in China)