According to recent news, my country's first underwater cable-laying robot with an operating speed of kilometers per hour, developed by the Guangdong Power Grid Company of the State Grid Corporation of China, recently completed its launching test.
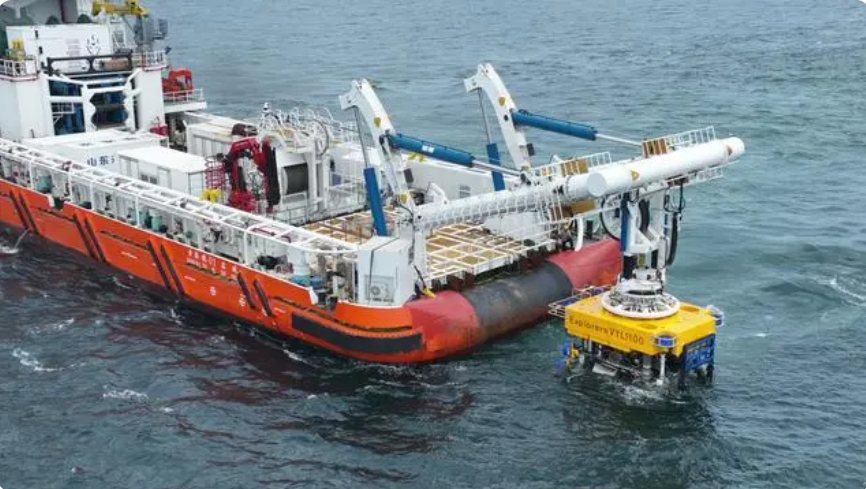

It is reported that this robot integrates crawler and sled walking functions, and has the integrated operation capability of "search-ditch-burying", with an operating speed of up to 1000 meters per hour. Its core components have achieved 100% autonomous control, indicating that the project has moved from theoretical research to the prototype stage.
According to reports, in order to deal with the problems of poor submarine cable perception and short continuous operation time of underwater cable laying robots, the project team innovatively proposed a submarine cable detection and positioning method of "acoustic-optical-magnetic-electric" multi-mode information fusion, breaking through the anti-interference navigation technology problem of multi-sensor combination, and solving the problem of underwater cable laying robots' difficulty in searching and locating submarine cables in low-visibility underwater environments and the failure of near-bottom underwater navigation.
Multi-sensor fusion perception breaks through anti-interference navigation technology
It is well known that underwater cable-laying robots face complex and changeable underwater environments when performing operations, which puts extremely high demands on the robot's navigation system. Among them, the anti-interference navigation technology of multi-sensor combination is the key.
Traditionally, underwater cable-laying robots have many difficulties in submarine cable perception and continuous operation, especially in low-visibility underwater environments, where the search and positioning of submarine cables become particularly difficult, and near-bottom underwater navigation often fails.
In order to solve these problems, the R&D team innovatively proposed a submarine cable detection and positioning method with "acoustic-optical-magnetic-electric" multi-mode information fusion.
This method achieves comprehensive perception of the underwater environment by fusing information from multiple sensors, such as sound waves, optics, magnetic fields, and currents. The complementarity and redundancy of information from multiple sensors not only improves the accuracy and reliability of the navigation system, but also effectively enhances its anti-interference ability. Even in a complex and changeable underwater environment, the robot can accurately find the location of the submarine cable and perform stable navigation and operations.
This paper is from Ulink Media, Shenzhen, China, the organizer of IOTE EXPO (IoT Expo in China)